ENR 1.4 ATS AIRSPACE CLASSIFICATION AND DESCRIPTION
1 Air Traffic Services Airspace Classification
2 ATS Airspace Descriptions
-
Definition
All airways above FL200 up to and including FL600 within Incheon FIR that are designated by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport.
-
Operating Rules and Pilot Requirements
Unless otherwise authorized by the Minister of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, all pilots must operate their aircraft under IFR and hold instrument certificates and ratings.
-
Equipment Requirements
Unless otherwise authorized by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, aircraft must be equipped with radio equipment prescribed by Article 107 of Enforcement Rules of the Aviation Safety Act to operate in Class A Airspace. Application of this
Equipment Requirement is temporarily waived for military aircraft. -
Separation Provided
IFR separation is provided to all aircraft.
-
Service Provided
Air Traffic Control service is provided to all aircraft.
-
Flight Procedures
The pilot must contact Incheon/Daegu ACC on the appropriate frequency prior to entering Class A Airspace and obtain an ATC clearance and thereafter maintain communications with ATC continuously while in Class A Airspace.
Military VFR aircraft of Republic of Korea will observe the Flight Information Notification procedures specified on the Letter of Agreement between Incheon ACC and the facilities concerned instead of following Class A airspace flight procedures, when the aircraft transit an airway of Class A airspace.
-
Definition
Generally, that airspace surrounding the nation's busiest airports/airbase (hereinafter referred to as airports) in terms of IFR operations or passenger transportation that have operational control towers and radar approach control; and designated by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport within Incheon FIR.
Incheon Airports
The airspace consists of a 5 NM(9.3KM) radius of 372745N 1262621E including areas which are extended northbound from 373156N 1261525E - 373721N 1262500E - 373241N 1262713E - 372852N 1262003E and southbound from 372247N 1262526E - 372654N 1263222E - 372339N 1263710E - 371815N 1262736E - 373156N 1261525E area that extends from the surface up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL, and 10NM (18.5KM) radius of 372745N 1262621E including areas which are extended northbound from 373454N 1261246E - 374019N 1262221E - 373721N 1262500E - 373156N 1261525E and southbound from 371815N 1262736E - 372339N 1263710E - 371917N 1264102E - 371353N 1263128E - 373454N 1261246E area that extends from 1 000 FT above the airport elevation up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL, and a 20 NM(27KM) radius shelf area that extends from 5 000 FT above the airport elevation up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL.
Gimpo Airport
The airspace consists of a 5NM radius of 373325N 1264751E including areas which are extended northbound from 373646N 1263926E - 373944N 1264310E - 373803N 1264518E - 373458N 1264142E, and southbound from 372840N 1264938E - 373036N 1265252E - 372907N 1265444E - 372652N 1265153E - 373646N 1263926E area that extends from the surface up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL, and a 10 NM(18.5KM) radius shelf area that extends from 1 000 FT above the airport elevation up to and including 10000 FT AMSL, and a 20 NM(27KM) radius shelf area that extends from 5 000FT above the airport elevation up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL.
Gimpo Airport Class B airspace
Jeju Airport
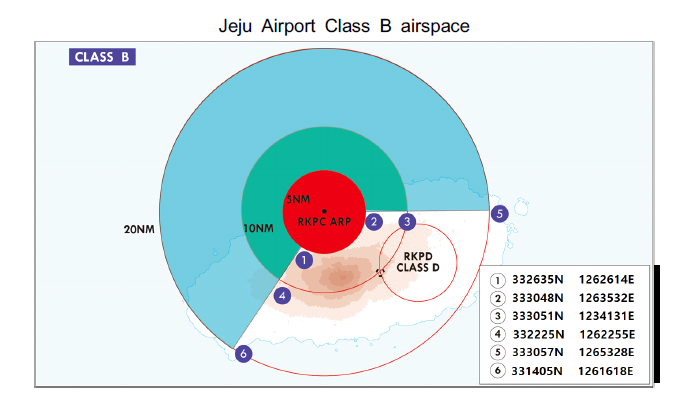
The airspace consists of a 5 NM radius of RKPC ARP (333044N 1262934E) area that extends from the surface up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL, and 332635N 1262614E ~ A clockwise arc, radius 5NM centered on ARP ~ 333048N 1263532E ~ 333051N 1264131E ~ A counterclockwise arc, radius 10 NM centered on ARP ~ 332225N 1262255E ~ 332635N 1262614E areas that extend from 1 000 FT AMSL up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL, and 332225N 1262255E ~ Clockwise arc, radius 10 NM centered on ARP ~ 333051N 1264131E ~ 333057N 1265328E ~ A counterclockwise arc, radius 20 NM centered on ARP ~ 331405N 1261618E ~ 332225N 1262255E area that extends from 2 000 FT AMSL up to and including 10 000 FT AMSL.
Jeju Airport Class B airspace
-
Operating Rules and Pilot Requirements
IFR and VFR flights are permitted and no specific pilot certification is required.
-
Equipment Requirements
Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, aircraft operating within Class B Airspace must be equipped with a two-way radio communications equipment and a radar beacon transponder with automatic altitude reporting equipment. Application of this Equipment Requirement is temporarily waived for military aircraft not equipped with a radar beacon transponder with automatic altitude reporting equipment.
-
Separation Provided
-
IFR and VFR aircraft are separated from all aircraft.
-
-
Service Provided
-
Air Traffic Control service is provided to all aircraft.
-
Traffic advisories and safety alerts services are mandatory provided to all aircraft.
-
Sequencing and separation services from other aircraft are provided to VFR pilots while operating within Class B Airspace.
-
If a route of flight for the separation between aircraft is extended beyond Class B Airspace, the pilot will be notified when the aircraft leaves or reenters the Class B Airspace.
-
Aircraft departing other airports within Class B Airspace will receive the same services provided to aircraft departing from the primary airport designated Class B Airspace.
-
-
Flight Procedures
-
All aircraft must contact the ATC facility prior to entering Class B Airspace, report their position, altitude, radar beacon code, destination, and request Class B service and thereafter maintain two-way communications with ATC while in Class B Airspace. Military VFR aircraft of Republic of Korea will observe the Flight Information Notification procedures specified on the Letter of Agreement between Incheon ACC and the facilities concerned instead of following Class B Airspace flight procedures, when the aircraft transit the Class B Airspace.
-
Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, a large turbine engine-powered airplane departing or landing an airport within airspace designated as Class B shall operate at or above the designated floors of Class B Airspace while flying within the lateral limits of Class B Airspace.
-
VFR aircraft must obtain a clearance to depart from an airport in Class B Airspace and advise the ATC facility of their intended altitude and route of flight.
-
Aircraft not landing or departing an airport within airspace designated as Class B may obtain an ATC clearance to transit the Class B airspace when the Operating Rules and Pilot and Equipment Requirements of Class B airspace are met and traffic conditions permit.
-
Unless otherwise authorized by ATC because of aircraft performance limitations, no person may operate an aircraft below 10 000 feet AMSL at an indicated airspeed of more than 250 knots. However, all aircraft arriving at Incheon and Gimpo airports within the Seoul TMA and Jeju airport shall be operated in accordance with each airport's flight procedure.
-
-
Satellite Airports Operations
-
Aircraft departing at a satellite airport will receive Classic B services after they have been radar identified and two-way radio communications have been established with the ATC facility for the Class B airspace.
-
Classic B services to aircraft proceeding inbound to a satellite airport will be discontinued when the aircraft is instructed to contact the ATC facility of the satellite airport.
-
Class D services are provided to aircraft in the airspace where Class B and Class D Airspace overlap.
-
-
Definition
Generally, that airspace surrounding those airports that have a large number of IFR operations or passenger enplanements and that have operational control towers and radar approach control facilities; and designated by the Minister of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs within Incheon FIR.
Gwangju, Sacheon, Gimhae, Wonju, Daegu, Yecheon, Gangneung, Jungwon, Seosan, Pohang, Gunsan Airports.
Gwangju, Sacheon, Wonju, Gangneung, Jungwon, Seosan, Pohang, Gunsan Airports.
The airspace consists of a 5 NM(9.3km) radius core surface area centered at the airport that extends from the surface up to 5 000 feet above the airport elevation, and a 10 NM(18.5km) radius shelf area that extends from 1 000 feet above the airport elevation to 5 000 feet above the airport elevation.
Gimhae Airports. The airspace consists of a 5 NM(9.3 km) radius core surface area centered at the airport including areas which are extended southbound from 350603N 1285427E - 350629N 1285918E - 350304N 1285944E - 350239N 1285453E area that extends from the surface up to 5 000 ft.
Daegu Airports. The airspace consists of a 5 NM(9.3 km) radius core surface area centered at the airport including areas which are extended southeastbound from 354924N 1284249E - 355243N 1284535E - 355030N 1284934E - 354712N 1284648E area that extends from the surface up to 5 000 ft.
Yecheon Airports. The airspace consists of a 5 NM(9.3 km) radius core surface area centered at the airport including areas which are extended eastbound from 363958N 1282658E - 364000N 1283035E - 363559N 1283039E - 363557N 1282702E area that extends from the surface up to 5 000 ft.
-
Operating Rules and Pilot Requirements
IFR and VFR flights are permitted and no specific pilot certification is required.
-
Equipment Requirements
Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, aircraft operating within Class C Airspace must be equipped with a two-way radio and a radar beacon transponder with automatic altitude reporting equipment. Application of this Article is temporarily waived for military aircraft not equipped with a radar beacon transponder with automatic altitude reporting equipment.
-
Separation Provided
-
Separation is provided to aircraft within the Class C Airspace after two-way radio communications and radar contact are established.
-
IFR aircraft are separated from VFR and other IFR aircraft, and VFR aircraft are separated from IFR aircraft. However, no separation services are provided to VFR helicopters from IFR helicopters.
-
-
Service Provided
-
ATC service is provided to IFR aircraft, and separation service from IFR aircraft is provided to VFR aircraft.
-
Arrival sequencing service is provided to all aircraft landing at an airport within Class C Airspace.
-
Traffic information is provided among VFR aircraft, and traffic avoidance advisories are provided upon VFR pilot requests if the controller's workload permits.
-
Unless pilots request the termination of the service, Class C services are provided to the pilots until the aircraft leaves that Class C airspace.
-
-
Flight Procedures
-
All aircraft must contact the ATC facility prior to entering Class C Airspace and give their position, altitude, radar beacon code, destination, and then request Class C service and a clearance, and thereafter maintain two-way radio communications while in Class C Airspace.
-
All pilots departing from an airport designated Class C Airspace must contact the ATC facility and thereafter maintain two-way radio communications until the aircraft leaves that Class C Airspace.
-
Unless otherwise authorized by ATC because of aircraft performance limitations, no person may operate an aircraft below 10 000FT AMSL at an indicated airspeed of more than 250 knots and at or below 2 500FT above the surface within 4NM of the airports at an indicated airspeed of more than 200 knots.
-
-
Satellite Airports Operations
-
Aircraft departing at satellite airports will receive Class C services after they have been radar identified and two-way radio communications have been established with the ATC facility.
-
Classic C services to aircraft proceeding inbound to a satellite airport will be discontinued when the aircraft is instructed to contact the ATC facility of the satellite airport.
-
Class D services are provided to aircraft in the airspace where Class C and D Airspace overlap.
-
-
Definition
Generally, the airspace designated by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport within Incheon FIR as follows:
-
The airspace consists of a 5NM(9.3KM) radius core surface area centered at the airport that extends from the surface up to 5 000FT above the airport elevation or the specific upper limits altitude of the airport control zone that have an operational control tower.
Cheongju Airports. The airspace consists of a 5 NM(9.3 km) radius core surface area centered at the airport including areas which are extended southwest-bound from 364004N 1272052E - 364151N 1272344E - 363841N 1272646E - 363654N 1272354E and northeast-bound from 364727N 1273246E - 364914N 1273539E - 364603N 1273841E - 364416N 1273548E area that extends from the surface up to 5 000 ft. -
All airways from MEA up to and including FL200.
-
The airspace other than Class B Airspace above 10 000 FT AMSL up to and including 18 500 FT AMSL within the Seoul TMA.
-
-
Operating Rules and Pilot Requirements
IFR and VFR flights are permitted and no specific pilot certification is required.
-
Equipment Requirements
Equipment Requirements Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, aircraft operating within Class D Airspace must be equipped with a two-way radio and a radar beacon transponder with automatic altitude reporting equipment. Application of this Article is temporarily waived for military aircraft not equipped with a radar beacon transponder with automatic altitude reporting equipment.
-
Separation Provided
-
Upon establishing two-way radio communications and radar contact, IFR aircraft are separated from VFR and other IFR aircraft.
-
No separation services are provided to VFR aircraft.
-
-
Service Provided
-
Traffic information in respect of VFR aircraft and ATC services are provided to IFR aircraft, and traffic avoidance advisories are provided to IFR aircraft upon pilots request.
-
Arrival sequencing service is provided to all aircraft landing at an airport within Class D Airspace.
-
Traffic information in respect of IFR aircraft is provided to VFR aircraft, and traffic avoidance advisories are provided to VFR aircraft upon pilots request.
-
Class D Airspace services are provided to the pilots until the aircraft lands at an airport within Class D Airspace or leaves the Class D Airspace.
-
-
Flight Procedures
-
1) All aircraft must contact the ATC facility prior to entering Class D Airspace and give their position, altitude, radar beacon code, destination, and then request Class D service and a clearance, and thereafter maintain two-way radio communications while in Class D Airspace. Military VFR aircraft of Republic of Korea will observe the Flight Information Notification procedures specified on the Letter of Agreement among the facilities concerned instead of following Class B airspace flight procedures, when the military VFR aircraft transit the Class D Airspace in Seoul TMA or airways of Class D Airspace.
-
2) All pilots departing from the airport designated Class D Airspace must contact the ATC facility concerned and thereafter maintain two-way radio communications until the aircraft leaves the Class D Airspace.
-
3) Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, pilots must operate their aircraft under IFR within airways of Class D airspace.
-
4) Unless otherwise authorized by ATC because of aircraft performance limitations, no person may operate an aircraft below 10 000FT AMSL at an indicated airspeed of more than 250 knots and at or below 2 500ft above the surface within 4NM of the airports at an indicated airspeed of more than 200 knots.
-
-
Satellite Airports Operations
ATC services in the airspace where Class D Airspace overlap other Class D Airspace are provided in accordance with the Letter of Agreement between the facilities concerned.
-
Definition
Generally, that controlled airspace designated by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport within Incheon FIR that is not Class A, Class B, Class C, or Class D as follows :
-
The airspace that extends from 1 000 FT above the surface or the sea level up to and including FL600 within the entire airspace over the territory(including the land areas and territorial waters) of Republic of Korea.
-
The airspace that extends from 5 00 FT above the sea level up to and including FL600 other than the entire airspace over the territory (including the land areas and territorial waters) of Republic of Korea.
-
-
Operating Rules and Pilot Requirements
IFR and VFR flights are permitted and no specific pilot certification is required.
-
Equipment Requirements
Though specific equipment is not required, aircraft must be equipped with an operable two-way radio capable of communicating with ATC.
-
Separation Provided
-
IFR aircraft are separated from other IFR aircraft.
-
No separation services are provided to VFR aircraft.
-
-
Service Provided
-
ATC service is provided to IFR aircraft, and traffic information will be provided to VFR aircraft to the extent possible.
-
Traffic information will be provided to VFR aircraft as the controller's workload situation permitting if two-way radio communications have been established.
-
-
Flight Procedures
-
IFR aircraft must obtain a clearance from ATC facility prior to entering Class E Airspace and maintain radio communications, and thereafter operate as instructed by ATC.
-
Maintaining two-way radio communications with ATC facility is not mandatory for military VFR aircraft.
-
Unless otherwise authorized by ATC, all pilots maintaining two-way radio communications with ATC facility within the Class E Airspace must operate their aircraft below 10 000 FT AMSL at an indicated airspeed of no more than 250 knots.
-
-
Definition
Generally, that uncontrolled airspace designated by the Minister of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs within Incheon FIR that is not Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, or Class E as follows:
-
The airspace that extends from the sea level or surface to below 1 000 FT above the surface or the sea level within the entire airspace over the territory(including the land areas and territorial waters) of Republic of Korea.
-
The airspace that extends from the sea level to below 5 500 FT above the sea level other than the entire airspace over the territory(including the land areas and territorial waters) of Republic of Korea.
-
The airspace above FL600 to unlimited.
-
-
Operating Rules and Pilot Requirements
IFR and VFR flights are permitted and no specific pilot certification is required.
-
Equipment Requirements
specific equipment is required.
-
Service Provided
Flight information service is provided upon pilot request.
3 Basic VFR Weather Minimums
No person may operate an aircraft under basic VFR when the flight visibility is less, or at a distance from clouds that is less, than that prescribed for the corresponding altitude and class of airspace as the following:
|
Airspace |
Flight Visibility |
Distance from Clouds | |
|
Class A |
Not Applicable |
Not Applicable | |
|
Class B Class C Class D Class E Class G |
At and above 3 050 M (10 000 FT) AMSL |
8 KM (5 SM) |
1 500 M (5 000 FT) horizontally, 300 M (1 000 FT) vertically. |
|
Below 3 050 m (10 000 FT) AMSL and >above 900 M (3 000 FT) AMSL or above 300 M (1 000 FT) above terrain, whichever is the higher. |
5 KM (3 SM) |
1 500 M (5 000 FT) horizontally, 300 M (1 000 FT) vertically. | |
|
Class B Class C Class D Class E |
At and below 900M (3 000FT) AMSL, or 300Mz (1 000FT) above terrain, whichever is the higher. |
8 KM (5 SM) |
1 500 M (5 000 FT) horizontally, 300 M (1 000 FT) vertically. |
|
Class G |
At and below 900 M (3 000 FT) AMSL, or 300m (1 000 FT) above terrain, whichever is the higher. |
5 KM (3 SM) |
Clear of cloud and with the surface in sight. |
4 Summary of ATS Airspace Classifications
|
Type of Category |
Class |
Designated areas and altitude |
Type of flight |
Separation provided |
Service provided |
Radio Communication requirement |
Subject to an ATC clearance |
|
Controlled |
A |
● All airways from above FL200 to FL600* |
IFR |
All aircraft |
ATC service |
Continuous two-way |
Yes |
|
B |
● Incheon airport* - Within 5NM including areas which are extended northbound from 373156N 1261525E - 373721N 1262500E - 373241N 1262713E - 372852N 1262003E and southbound from 372247N 1262526E - 372654N 1263222E - 372339N 1263710E - 371815N 1262736E - 373156N 1261525E(SFC~10 000 FT AMSL) - Within 5~10NM including areas which are extended northbound from 373454N 1261246E - 374019N 1262221E - 373721N 1262500E - 373156N 1261525E and southbound from 371815N 1262736E - 372339N 1263710E - 371917N 1264102E - 371353N 1263128E - 373454N 1261246E(1 000 FT AGL~10 000 FT AMSL) - Within 10~20NM(5 000 FT AGL~10 000 FT AMSL) ● Gimpo airport* - Within 5 NM including areas which are extended northbound from 373646N 1263926E - 373944N 1264310E - 373803N 1264518E - 373458N 1264142E, and southbound from 372840N 1264938E - 373036N 1265252E - 372907N 1265444E - 372652N 1265153E - 373646N 1263926E - Within 5~10 NM (1 000ft AGL~10 000ft MSL) - Within 10~20NM (5 000ft AGL~10 000ft MSL) ● Jeju Airport - A circle, radius 5NM centered at RKPC ARP (333044N 1262934E) : SFC ~ 10 000 FT AMSL - 332635N 1262614E - a clockwise arc, radius 5NM centered at ARP - 333048N 1263532E - 333051N 1264131E - a counterclockwise arc, radius 10NM centered at ARP - 332225N 1262255E - to the beginning : 1000 FT AMSL ~ 10 000 FT AMSL - 332225N 1262255E - a clockwise arc, radius 10NM centered at ARP - 333051N 1264131E - 333057N 1265328E - a counterclockwise arc, radius 20NM centered at ARP - 331405N 1261618E - to the beginning : 2 000 FT AMSL ~ 10 000 FT AMSL |
IFR VFR |
All aircraft |
ATC service |
Continuous two-way |
Yes | |
|
C |
● Radius of airports with APP Control** - Within 5 NM (SFC 5 000 ft AGL) - Within 5 10 NM (1 000 ft AGL ~ 5 000 ft AGL) |
IFR |
IFR from IFR IFR from VFR |
ATC service |
Continuous two-way |
Yes | |
|
VFR |
VFR from IFR |
● ATC service for separation from IFR ● VFR/VFR traffice information (and traffic avoidance advice on request) |
Continuous two-way |
Yes | |||
|
D |
● All airways from MEA up to and including FL200 ● Airspace from above 10 000 FT AMSL to FL185 within Seoul TMA, excluding Class B* ● Radius of airports none APP Control *** - Within 5 NM (SFC 5 000 ft AGL or the upper limits altitude of control zone) |
IFR |
IFR from IFR, IFR from VFR(RDO & RADAR CTC) |
● ATC service including traffic information about VFR flights (and traffic avoidance advice on request) |
Continuous two-way |
Yes | |
|
VFR |
NIL |
● Traffic information between VFR and IFR flights (and traffic avoidance advice on request) |
Continuous two-way |
Yes | |||
|
E |
● Controlled Airspace except Class A, B, C, and D - Airspace (Lands and Waters) : 1 000 ft ~ 60 000 ft from the surface of the earth or sea - Airspace over the high seas : 5 500 ft, from the surface of the sea ~ 60 000 ft MSL |
IFR |
IFR from IFR |
● ATC service ● Traffic information about VFR aircraft as far as practicable |
Continuous two-way |
Yes | |
|
VFR |
NIL |
● Traffic information as far as practicable |
No(EXC CIV ACFT) |
No | |||
|
Un-controlled |
G |
● Uncontrolled airspace except Class A,B,C,D and E - Airspace (Lands and Waters) : Below 1 000 FT from the surface of the earth or sea - Airspace over the high seas : Below 5 500 FT from the surface of the sea - The airspace above FL600 to unlimited. |
IFR VFR |
NIL |
● Flight information service |
No |
No |
* Though application of the flight procedures for Korean military mentioned on each Class is reserved, Korean military shall observe the Flight Information Notification procedures specified on the LOA between concerned facilities.
** Gimhae, Gwangju, Sacheon, Daegu, Gangneung, Jungwon, Seosan, Wonju, Yecheon, Gunsan and Pohang Airports(11)
*** Osan, Yangyang, Seoul, Cheongju, Suwon, Seongmu, Pyeongtaek, Ulsan, Yeosu, Mokpo, Muan, Uljin, Jeongseok, Jinhae, Icheon, Nonsan and Sokcho Airports(17)